EARSC EO Product Award 2018: industry contributions to the SDGs
The European Association of Remote Sensing Companies (EARSC) competition “European EO product of the year” rewarded Silex Clouds S.R.L, a start-up promoted by a group of researchers from the University of Rome, for developing the Dust Frequency Map product that provides a historical analysis (in amount of hours of impact) of dust storm occurrences divided by month, season, and year, over the last 12 years. The values expressed in the map represent –in amount of hours- a Dust Load Index (on the base of an historical/statistical analysis from the processing of thermal bands, evidencing an estimation of dust charge).
Dust Frequency Maps
The Dust Frequency Map product, developed by Silex Clouds S.R.L. provides a historical analysis (in amount of hours of impact) of Dust storm occurrences divided by month, season and year, over the last 12 years. The values expressed in the map represent –in amount of hours- a Dust Load Index (on the base of an historical/statistical analysis from the processing of thermal bands, evidencing an estimation of dust charge).
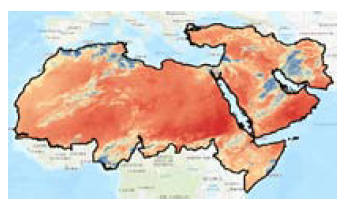
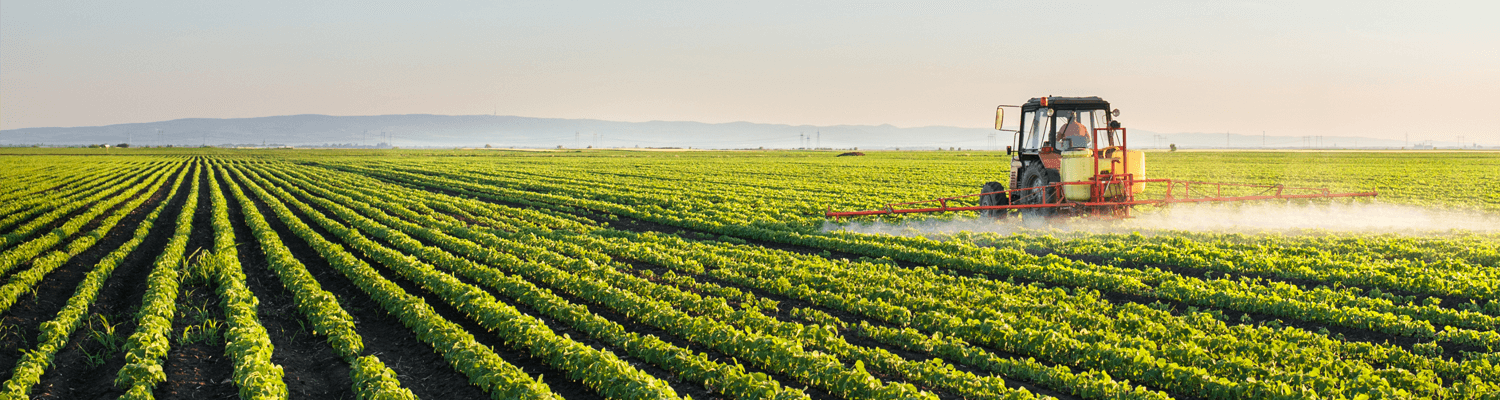
Spatial coverage
MENA (Middle East and North Africa) extended region: Western Sahara, Senegal, Mauritania, Morocco, Mali, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, Niger, Nigeria, Chad, Sudan, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somalia, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, West Bank, Syria, Turkey, Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Oman, Yemen. (Figure right: Dust Frequency Map in MENA region (example temporal resolution 1 month)).
Problem to solve
To define the electricity generated in output of a photovoltaic (PV) system, a set of variables need to be set, as: PV yield or efficiency, solar radiation and performance ratio (coefficient for losses). The optimum PV yield, defined by the solar insolation, will be determined by environmental factors and the particular PV installation design, which can be separated into alterable and unalterable factors. In this context, the presence of dust in the atmosphere and soiling losses (loss in power resulting from particles that cover the surface of PV modules) plays an important role in the analysis of the PV system efficiency prevision. Daily PV energy losses along a year caused by dust deposition can be from 5% to 30%. As an unalterable environmental factor, the possibilities to manage the impact of this phenomenon are focused on: the identification of dust historical distribution, and the real time monitoring and forecasting.
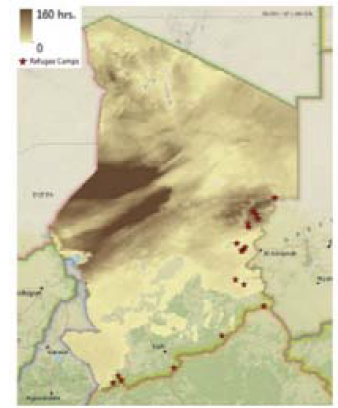
The Dust Monitoring Service (DMS), focused mainly in the MENA region, is oriented to assist in the management of PV Solar Parks under dust/sand conditions that affect the performance of solar panel energy projections and effective production, daily.
This product will support the following SDGs:
Silex Clouds S.R.L. recognize several SDGs, such as the ones relating to Energy, Climate Change, and Cities, as the SDGs towards which this product can contribute the most:
Goal 7 (energy): helping improve efficiency in the management of the renewable energy infrastructures and best potential locations. At the same time, providing innovative services and datasets from Earth observation satellites, mainly in least developed countries. An indicator could exhibit the adoption of better energy management practices, also timely identifying critical energy infrastructure under harsh and persistent dust conditions.
Goal 13 (climate): helping identify changing weather patterns and with the full DMS, the real time monitoring of extreme dust storm events. Also giving support for erosion and soil degradation monitoring and impact on agriculture. Fine dust particles are the most important sediment for soil fertility. They contain vital nutrients and offer resistance to drought. For instance, monitoring the expansion of dust-affected areas can support the Consultative Group for International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) Research Program on Dryland Systems. The indicators could reveal the amount of dust events putting into evidence at the same time, potential patterns. And also according to these patterns agricultural areas under risk.
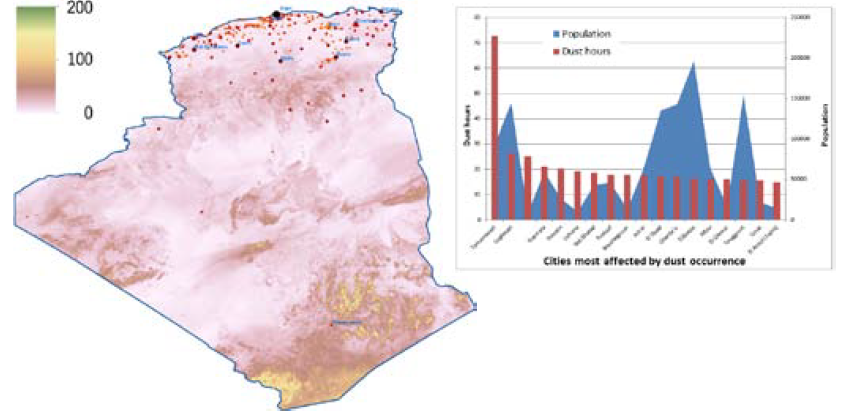
Goal 11 (cities): helping deal with challenges related to city infrastructures and services, such as transport systems. Providing support to improve road safety, identifying most impacted areas and their seasonality. Also with the full DMS, real time railways status reports (related to the presence of dust events) could help reduce risks of accidents (Secretariat of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification – UNCCD 2002). A dust storm cannot only impact the area surrounding its origin, but can also impact land and people, a great distance away, where the dust finally settles. These transboundary movements can pose challenges when formulating policies pertaining to dust storm mitigation (i.e. vegetation restoration efforts) or early warning communication (UN Environment, 2013). An indicator could reveal the cities that are most affected by dust events.
About Silex Clouds S.R.L.:
Silex Clouds is an innovative Italian start-up promoted by a group of researchers from the University of Rome. The company offers a set of services related to the exploitation of Earth Observation (EO) satellites datasets, and is composed by an heterogeneous group of professionals related to Aerospace Engineering, Remote Sensing technologies and Geographic Information Systems management.
Silex Clouds S.R.L. highlights the need to facilitate access to information obtainable from satellite data. Despite the enormous amount of remote sensing data currently available, their use by end-users is still significantly reduced. It is therefore proposed to increase the efficiency of the processes for the generation of information obtained from satellite data, creating a service aimed at providing information in real time, facilitating the accessibility and ingestion of these products in end-users systems (i.e.: API requests), giving at the same time the possibility to differentiate services companies portfolios with innovative added value products.

























